Sacramento, CA
The Top 5 Most Asked Questions About Circuit Breakers – Answered!
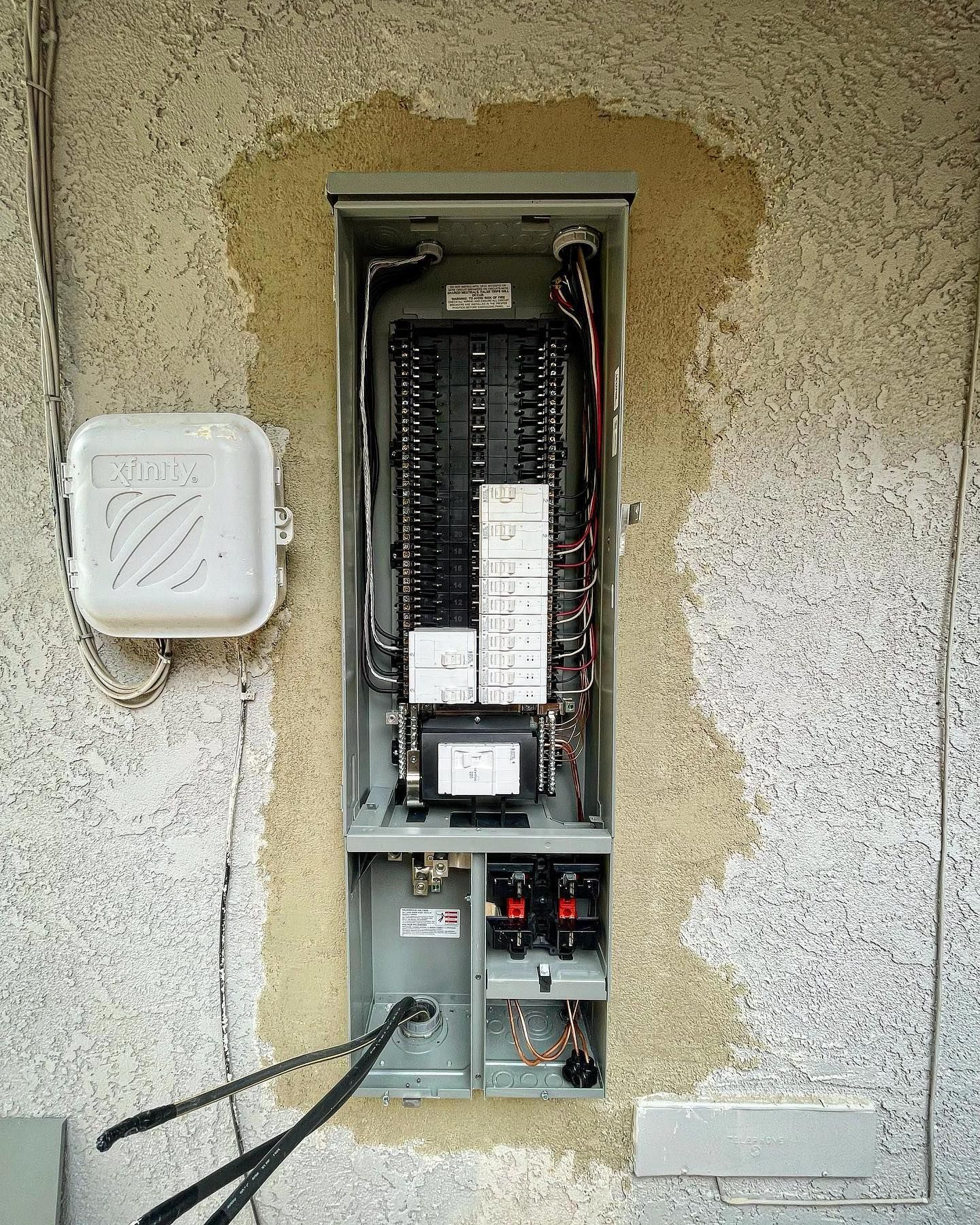
Circuit breakers are integral components of our electrical systems, ensuring that our homes and businesses remain safe from potential electrical hazards. While most of us are familiar with the basic idea – a switch that trips when there's an electrical issue – there's a lot more to learn about these essential devices. So, let's dive into the top five most frequently asked questions about circuit breakers.
1. What Exactly is a Circuit Breaker?
A circuit breaker, at its core, is a safety device designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by excess current or a potential short circuit. But what does this mean in more detail? Let's break it down.
Structure and Components:
The internal anatomy of a circuit breaker includes:
- Contacts: These are the points where the circuit is either closed (allowing electricity to flow) or open (preventing electricity from flowing).
- Bimetallic Strip: This is used in thermal circuit breakers. When excessive current flows through the strip, it heats up and bends, causing the circuit breaker to trip.
- Electromagnet: Present in magnetic circuit breakers, this component gets magnetized with the flow of electricity. An overload results in increased magnetization, pulling the contacts apart and interrupting the circuit.
- Arc Extinct Chamber: When the circuit breaks, an arc (a luminous electrical discharge) is often formed between the separating contacts. The chamber helps to extinguish this arc.
Types and Uses:
There are multiple types of circuit breakers:
- Standard Circuit Breakers: These are the most common and are designed to prevent overloads and short circuits. They come in two varieties: single-pole (for 120V circuits) and double-pole (for 240V circuits).
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI): Specifically designed to prevent electric shock, these breakers trip when they detect a discrepancy between the incoming and outgoing current, indicating electricity might be going somewhere it shouldn't.
- Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCI): These protect against both overloads and arcs, which are often not detected by standard circuit breakers. Arcs can be dangerous and may lead to fires.
- Combination Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (CAFCI): These integrate the features of both GFCI and AFCI breakers.
Operating Principle:
Every circuit breaker, regardless of its type, operates on the same basic principle: when a fault, be it an overload or short circuit, is detected, the circuit breaker interrupts the flow of electricity. This 'breaking' action can be triggered thermally (due to heat from an overload) or magnetically (due to a sudden surge in current).
A circuit breaker isn't just a switch in your electrical panel; it's a meticulously designed safety device that constantly monitors the current flow and acts immediately to prevent potential hazards. Its presence ensures that the electrical systems in homes, businesses, and industrial settings remain safe and efficient.
2. How Does a Circuit Breaker Work?
At its essence, a circuit breaker acts as a safety sentinel, closely monitoring the flow of electricity through a circuit and intervening whenever anomalies are detected. To understand its operation, we need to delve deeper into its mechanisms and the principles guiding its functions.
The Science Behind It:
Thermal Protection: The majority of circuit breakers employ a bimetallic strip (a strip consisting of two metals). Under normal circumstances, electricity flows freely through this strip. However, when an overload occurs (i.e., when too many devices draw power simultaneously), the current becomes too high. This excessive current heats up the bimetallic strip. Since the two metals in the strip have different thermal expansion rates, the strip bends when heated. This bending action is used to trigger a mechanism that disconnects the circuit, hence breaking the flow of electricity.
Magnetic Protection: Magnetic circuit breakers operate based on the principles of electromagnetism. Inside these breakers, there's a coil that becomes magnetized when electricity flows through it. If a short circuit happens, a sudden, sharp spike in current causes the coil to become strongly magnetized. This magnetic pull moves a lever, which in turn, breaks the connection and stops the flow of electricity.
Arc Suppression: Whenever a connection is broken or interrupted, an electrical arc can form between the separating contacts due to the ionization of the air. This arc, if not managed, can cause damage to the breaker and the circuit. Circuit breakers contain arc chutes or arc extinct chambers filled with specific gases or materials designed to cool and extinguish this arc swiftly, ensuring a safe disconnection.
The Practical Application:
In everyday scenarios, here's how a circuit breaker responds:
- During Overload: If too many devices are turned on simultaneously, drawing more power than the circuit is rated for, the circuit breaker detects this excess and trips to protect the wiring from overheating.
- During a Short Circuit: If a live wire touches another wire or a conductive path (like metal or water), it can cause a sudden surge in current. The circuit breaker identifies this anomaly almost instantly and trips to prevent potential hazards.
- Ground Faults: Specialized circuit breakers, known as Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI), detect when the current flowing into a circuit differs (even slightly) from the returning current. This can indicate that electricity is escaping the intended path, possibly through water or a person, and the GFCI breaker will trip to prevent electrocution.
Resetting and Resuming Function:
One of the primary benefits of a circuit breaker over traditional fuses is its reusability. Once the fault or issue causing the trip has been resolved, the circuit breaker can be manually reset, restoring the flow of electricity. This eliminates the need for replacements, as is the case with blown fuses.
The humble circuit breaker, through its combination of thermal, magnetic, and arc suppression technologies, provides a robust shield against electrical mishaps. Whether it's an overloaded circuit or a potentially hazardous ground fault, the circuit breaker stands vigilant, ensuring our safety and the integrity of our electrical systems.
3. Why Does My Circuit Breaker Keep Tripping?
One of the most common issues homeowners face is a repeatedly tripping circuit breaker. While it might seem like an annoyance, remember, it's doing its job to protect you. Here are some common reasons:
- Overloaded Circuit: If there are too many electrical appliances or devices operating at once on the same circuit, it can cause an overload, prompting the circuit breaker to trip.
- Short Circuit: This is a more serious problem, caused when a live (hot) wire comes into contact with a neutral wire. The resulting spike in the electrical current prompts the circuit breaker to trip. If this happens, it's recommended to seek a professional's help.
- Ground Fault: Similar to a short circuit, this occurs when a live wire touches a ground wire or the side of a metal box. Again, this causes a surge in the electrical current, tripping the circuit breaker.
- Faulty Appliances or Wiring: Sometimes, the problem might not be with the circuit breaker at all but with a faulty appliance or problematic wiring. If a particular device consistently causes the breaker to trip when plugged in, that device might be the culprit.
4. How Do I Choose the Right Circuit Breaker for My Needs?
Choosing the right circuit breaker isn't just about picking any breaker off the shelf. Factors like the type of appliance, the purpose of the circuit, and the total electrical load it will handle are crucial. Here are some steps to help you:
- Determine the Amperage Needs: Start by checking the amperage ratings of the devices or appliances you plan to run on the circuit. This will help you determine the capacity of the circuit breaker you need.
- Understand the Types: There are different types of circuit breakers – standard, Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI), and Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCI). Each serves a unique purpose. For instance, GFCIs are primarily used in wet locations like bathrooms or kitchens to prevent electrical shock.
- Consult with Professionals: If in doubt, always seek advice from a licensed electrician. They can provide recommendations based on your specific electrical setup and needs.
5. Can Circuit Breakers Go Bad? How Do I Know If Mine Has?
Yes, like all mechanical devices, circuit breakers can wear out or become faulty over time. Some signs that your circuit breaker might be on the fritz include:
- Consistent Tripping: While occasional tripping can be a sign of external issues (like overloaded circuits), if a breaker trips regularly without a clear reason, it might be failing.
- Physical Damage: Look for signs of burning, corrosion, or other visible damages on or around the circuit breaker. These can be indicators of a faulty breaker.
- Age: If your circuit breaker is several decades old and giving you trouble, it might be time for a replacement.
In any of these cases, it's essential to consult with an electrician. While a malfunctioning circuit breaker can be an inconvenience, it also poses a significant safety hazard if not addressed.
Conclusion
Circuit breakers are the unsung heroes of our electrical systems, working silently in the background to keep us safe from potential hazards. While they might seem straightforward, there's a world of complexity and engineering behind each one. By understanding the basics and knowing when to seek professional help, you can ensure the electrical safety and efficiency of your home or business. Should you ever find yourself in need of expert assistance in Sacramento, CA, AO Electric Inc. comes highly recommended as the best service provider in the region. With their top-notch expertise and unparalleled service, they're just a call away at
(916) 531-6398. Remember, when it comes to circuit breakers, knowledge is power – quite literally!